Copain Keel and centerboard
Sailboat specifications
The Copain is a 17’2” (5.25m) cruising sailboat designed by Henri Amel (France). She was built between 1962 and 1968 by Amel (France). The Keel and centerboard version features a centerboard inside of a short fin-keel allowing shoal draft while maintaining upwind capabilities.
The Copain is as well listed, on Boat-Specs.com, in Fin keel version (see all the versions compared).
The Copain is as well listed, on Boat-Specs.com, in Fin keel version (see all the versions compared).
Copain's main features
- Model
- Copain
- Version
- Keel and centerboard
- Hull type
- Monohull
- Category
- Cruising sailboat
- Sailboat builder
- Sailboat designer
- Country
- France
- Construction
- Hull and deck: GRP (glass reinforced polyester)
- Number of hulls built
- About 50
- First built hull
- 1962
- Last built hull
- 1968
- Appendages
- Centerboard : pivoting centerboard in the keel
- Helm
- Single tiller
- Rudder
- Single transom hung rudder
- Unsinkable
- Yes
- Trailerable
- Yes
- Standard public price ex. VAT (indicative only)
- N/A €
Copain's main dimensions
- Hull length
- 17’ 2”5.25 m
- Waterline length
- 16’4.88 m
- Beam (width)
- 5’ 11”1.8 m
- Waterline beam (width)
- 5’ 4”1.62 m
- Draft
- 3’ 4”1.02 m
- Draft when appendages up
- 1’ 10”0.56 m
- Light displacement (MLC)
- 1058 lb480 kg
- Ballast weight
- 397 lb180 kg
Copain's rig and sails
- Upwind sail area
- 172 ft²16 m²
- Downwind sail area
- 269 ft²25 m²
- Mainsail area
- 75 ft²7 m²
- Genoa area
- 97 ft²9 m²
- Solent area
- 65 ft²6 m²
- Jib area
- 32 ft²3 m²
- Symmetric spinnaker area
- 194 ft²18 m²
- Rigging type
- Sloop Marconi masthead
- Mast configuration
- Deck stepped mast
- Rotating spars
- No
- Number of levels of spreaders
- 1
- Spreaders angle
- 0 °
- Spars construction
- Aluminum spars
- Standing rigging
- 1x19 strand wire continuous
Copain's performances
- Upwind sail area to displacementiThe ratio sail area to displacement is obtained by dividing the sail area by the boat's displaced volume to the power two-thirds.
The ratio sail area to displacement can be used to compare the relative sail plan of different sailboats no matter what their size.
Upwind: under 18 the ratio indicates a cruise oriented sailboat with limited performances especially in light wind, while over 25 it indicates a fast sailboat. - 281 ft²/T26.1 m²/T
- Downwind sail area to displacementiThe ratio sail area to displacement is obtained by dividing the sail area by the boat's displaced volume to the power two-thirds.
The ratio sail area to displacement can be used to compare the relative sail plan of different sailboats no matter what their size. - 439 ft²/T40.78 m²/T
- Displacement-length ratio (DLR)iThe Displacement Length Ratio (DLR) is a figure that points out the boat's weight compared to its waterline length. The DLR is obtained by dividing the boat's displacement in tons by the cube of one one-hundredth of the waterline length (in feet).
The DLR can be used to compare the relative mass of different sailboats no matter what their length:
a DLR less than 180 is indicative of a really light sailboat (race boat made for planning), while a DLR greater than 300 is indicative of a heavy cruising sailboat. - 117
- Ballast ratioiThe Ballast ratio is an indicator of stability; it is obtained by dividing the boat's displacement by the mass of the ballast. Since the stability depends also of the hull shapes and the position of the center of gravity, only the boats with similar ballast arrangements and hull shapes should be compared.
The higher the ballast ratio is, the greater is the stability. - 38 %
- Critical hull speediAs a ship moves in the water, it creates standing waves that oppose its movement. This effect increases dramatically the resistance when the boat reaches a speed-length ratio (speed-length ratio is the ratio between the speed in knots and the square root of the waterline length in feet) of about 1.2 (corresponding to a Froude Number of 0.35) . This very sharp rise in resistance, between speed-length ratio of 1.2 to 1.5, is insurmountable for heavy sailboats and so becomes an apparent barrier. This leads to the concept of "hull speed".
The hull speed is obtained by multiplying the square root of the waterline length (in feet) by 1.34. - 5.36 knots
Copain's auxiliary engine
- Engine(s)
- 1 outboard engine
- Engine(s) power (min./max.)
- 3 HP / 5 HP
- Fuel type
- Gas
Copain's accommodations and layout
- Cockpit
- Closed aft cockpit
- Berth(s)
- 2


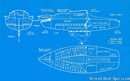





Amel Copain interior and accommodations - - 7/7
Picture extracted from the commercial documentation © Amel
Picture extracted from the commercial documentation © Amel
Similar sailboats that may interest you:
Sailboats
First built hull
Hull length
1985
23’ 7”7.2 m
1978
17’ 11”5.45 m
1977
18’ 10”5.74 m
2000
18’5.49 m
1961
22’ 7”6.9 m
1962
17’ 2”5.25 m
1985
22’ 7”6.9 m
1994
16’ 7”5.05 m
1964
19’ 10”6.05 m
1976
19’ 8”6 m
1978
19’ 8”6 m
1973
20’ 4”6.2 m
1979
19’ 8”6 m
1979
24’ 11”7.58 m
1989
20’ 8”6.3 m